

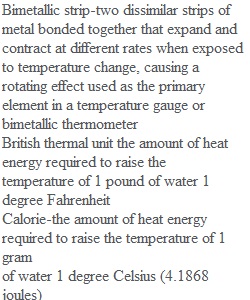
Q A-Bimetallic strip-two dissimilar strips of metal bonded together that expand and contract at different rates when exposed to temperature change, causing a B-rotating effect; used as the primary element in a temperature gauge or bimetallic thermometer, p. 51. C-British thermal unit (BTU)--the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 pound of water 1 degree Fahrenheit, p. 44. D-Calorie-the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius (4.1868 joules), p. 44. Celsius/centigrade scale of measurement to E-determine temperature; freezing point of water is 0 degrees Celsius (C), and the boiling point of water is at 100 degrees p. 47 F-Conduction--the transfer of heat through matter via vibrational motion; exchange media must be in direct contact, p. 44. G-Convection-the transfer of heat through the circulation or movement of a liquid or a gas, p. 44. H-Fahrenheit-scale of measurement to determine temperature; freezing point of water is 32 degrees Fahrenheit (F), and the boiling point of water is at 212 degrees F, p. 47. I-Filled thermal system-a temperature sensing bulb filled with a liquid, vapor, or ga and connected by means of a capillary tube to a pressure measuring element, p.5 J-Glass stem thermometer-a temperature measuring device constructed of a glass bulb and a capillary (small) tube made of glass with a numbered scale; the bulb and the capillary tube contain a liquid such as mercury or colored alcohol that expands, allowing a reading to be made from the etched scale on the length of th. K-tube; usually utilized in laboratory settings for calibration, p. 49. L-Heat-added energy that causes an increase in the temperature of a material (sensil heat) or a phase change (latent heat); the transfer of kinetic energy to increase the temperature of a substance via the process of conduction, convection, or radiation, p. 44. M-Infrared thermometer-a device that infers temperature using thermal radiation emitted by the substance being measured; also called pyrometer, p. 50. N-Kelvin-scale of measurement that is sometimes called an absolute scale because 0 Kelvin (K) is the point at which no heat o-exists; freezing point of water is 273 K and boiling point of water is 373 K, p. 47. P-Pyrometer-see infrared thermometer, p. 50. Q-Radiation-the transfer of heat energy through electromagnetic waves, p. 44. R-Rankine-an absolute scale of measurement to determine temperature; freezing P of water is 492 degrees Rankine (R) and boiling point of water is 672 degrees R. S-Resistance temperature detector (RTD)-primary element that measures temperature changes in terms of electrical resistance, p. 52. Temperature the average kinetic energy of a material, the indication of heat ene available to flow between bodies of differing temperatures, p.43. T-Temperature differential (deltaT or AT)-difference between two related temperatures or between temperatures measured at two different points, p. 46. U-Temperature gauge-an independent analog device with a sensing element such as a bimetallic strip, bourdon tube, or bellows that is linked to a pointer displaying the temperature on a calibrated face, p. 56. Thermistor a type of resistor used to measure temperature changes, relying on the change in its resistance with changing temperature, p. 54. Thermocouple-primary element consisting of two wires of dissimilar metals connected at one end; when it is exposed to heat, it generates a voltage proportional to the change in temperature, p. 53. V-Thermowell-a thick walled, typically stainless steel device shaped like a tube, wl- is inserted into a hole in piping or equipment; it is specifically prepared to house temperature sensing and measuring element, p. 55. 1-Bimetallic strip 2-British thermal unit (BTU) 3-Calorie 4-Celsius/centigrade 5- Conduction 6-Convection 7-Fahrenheit 8-Fill thermal system 9-Glass stem thermometer 10-Heat 11-Infrared thermometer 12-Kelvin 13 Pyrometer 14-Radiation 15-Rankine 16- Resistance temperature detector 17-Temperature 18- Temperature differential 19-Thermowell
View Related Questions